Body immunity against wounds
Date : 19 May 2024
As the largest organ of the body, the skin is our first line of defense against the outside world. This physical barrier protects us from pathogens, harmful substances and physical damage. However, our skin is also vulnerable to scarring. Wounds can be caused by cuts, burns, punctures, scratches and other injuries.
Although wounds are a natural part of life, it is important to take proper care of them to prevent infection and other complications. Fortunately, our bodies have a sophisticated immune system that works naturally to heal wounds.
In this article, we will examine the body’s defense mechanisms against wounds and strategies to strengthen the body’s immunity for faster and more effective healing of wounds.
The body’s defense mechanisms against wounds
When a wound is created, our body immediately takes action to repair it. This process includes different steps that are carried out by different cells, molecules and systems of the body.
Some of the key steps in wound healing are:
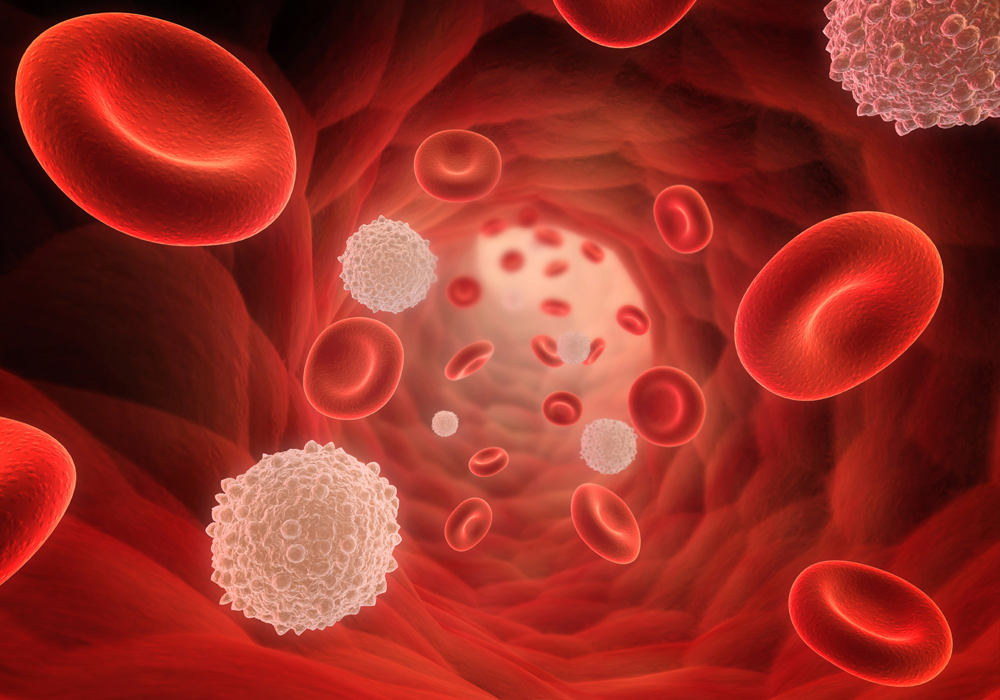
Hemostasis: The first step in wound healing is to stop bleeding. This is done by platelets and blood clotting factors.
Inflammation: After the bleeding stops, the body responds with a process called inflammation. This process includes redness, swelling, warmth, and pain. Inflammation helps white blood cells destroy bacteria and other pathogens.
New tissue growth: At this stage, new skin cells begin to grow to fill the damaged area.
Regeneration: Eventually, the body begins to regenerate the damaged tissue. This process involves the restoration of collagen and elastin, the proteins that give the skin strength and flexibility.
Strengthening the body’s immunity for faster healing of wounds
Various factors can affect the speed and quality of wound healing. Some of these factors are:
Age: With age, the wound healing process becomes slower.
Health status: Some diseases, such as diabetes and malnutrition, can impair wound healing.
Medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids, can slow wound healing.
Nutrition: A healthy diet rich in vitamins, minerals and protein can help wounds heal faster.
Smoking: Smoking impairs blood flow and can slow wound healing.
Stress: Stress can weaken the immune system and impair wound healing.
In addition, you can help boost your immune system for faster wound healing by taking some simple steps:
Keep the wound clean and dry.
Use the right dressing.
Protect the wound from sunlight.
Avoid smoking and alcohol.
Have a healthy and balanced diet.
Get enough sleep.
Control your stress.
See your doctor if you notice any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, pus, or fever.
Conclusion
The body’s immunity plays an essential role in wound healing. By understanding the body’s defense mechanisms and taking steps to strengthen the body’s immunity, you can help wounds heal faster and more effectively.